- Minification removes unnecessary characters from HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files without changing their functionality.
- Compression (Gzip and Brotli) encodes files in a more efficient way, significantly reducing their size.
- Use both minification and compression for maximum file size reduction.
- Minification is typically done as part of your build process or using online tools.
- Compression is typically enabled on the web server.
- Brotli offers better performance, however, Gzip is still used.
After images, your website’s code files (HTML, CSS, and JavaScript) are often the next biggest contributors to page size. Minification and compression are two crucial techniques for reducing the size of these text-based files, leading to faster download times and improved page speed. These techniques are relatively easy to implement and can have a significant impact on performance.
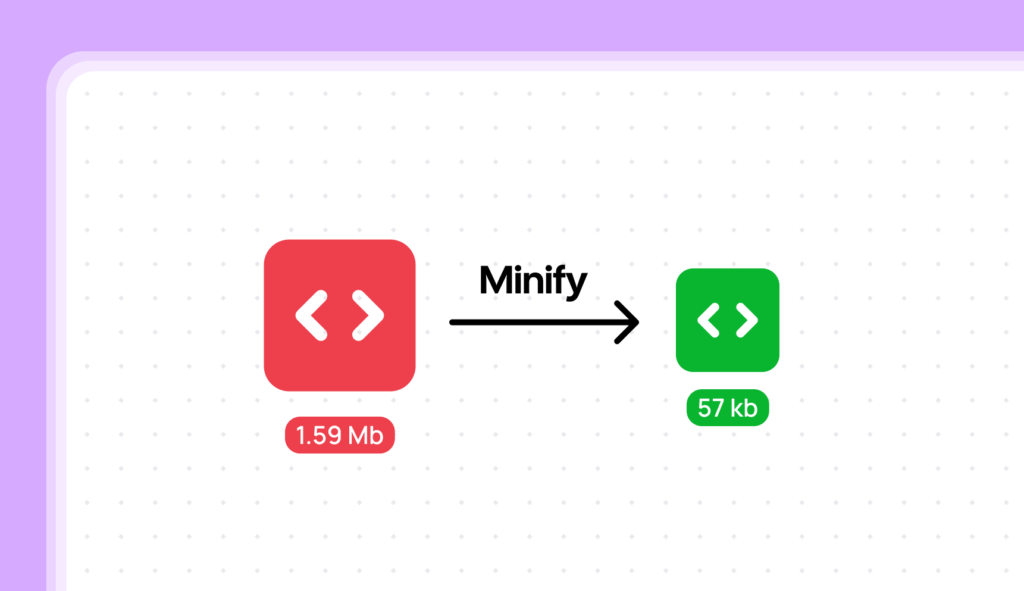
What is Minification?
Minification is the process of removing unnecessary characters from your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code without changing its functionality. These unnecessary characters include:
Why Minify?
Example (Before Minification – CSS):
/* This is a CSS comment */
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif; /* Set the font */
background-color: #f0f0f0;
margin: 0;
padding: 20px;
}
h1
color: #333; /* Dark gray */
font-size: 2em;
}Example (After Minification CSS):
body{font-family:Arial,sans-serif;background-
color:#f0f0f0;margin:0;padding:20px}h1{color:#333;font-size:2em}Example (Before Minification HTML):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My Website</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Hello, world! </h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>Example (After Minification HTML):
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><title>My Website</title></head><body>
<h1>Hello, world!</h1><p>This is a paragraph.</p></body></html>Example (Before Minification Javascript):
// Function to add two numbers
function addNumbers(a, b) {
// Return the sum
return a + b;
}
// Call the function
let result = addNumbers(5, 3);
// Display the result
console.log("The result is: " + result);
Example (After Minification Javascript):
function addNumbers(a,b){return a+b;}let
result=addNumbers(5,3);console.log("The result is: "+result);Notice how the minified code is much harder to read for humans, but it works exactly the same way for the browser.
Tools for Minification:
1. Online Minifiers:
2. Build Tools:
3. Task Runners:
4. Code Editors and IDEs:
5. WordPress plugins:
What is Compression? (Gzip and Brotli)
While minification reduces file size by removing unnecessary characters, compression reduces file size by encoding the data in a more efficient way. Think of it like zipping a file on your computer. The most common compression methods used for web files are Gzip and Brotli.
How Compression Works (Simplified):
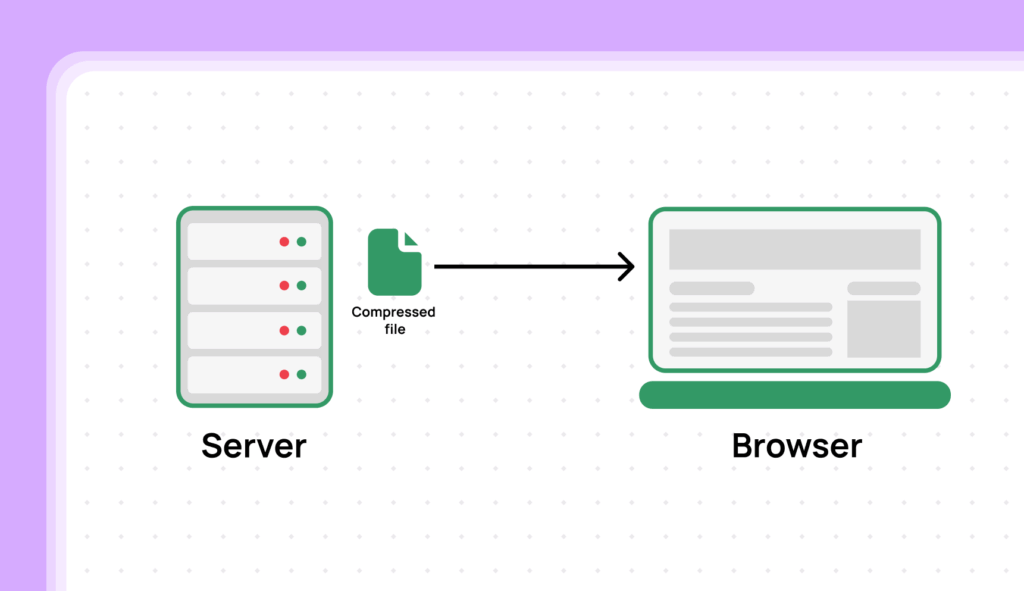
Compression algorithms look for repeating patterns in the text-based files (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) and replace them with shorter codes. The browser then decompresses the files on the fly when it receives them. This happens transparently to the user.
Why Use Compression?
Enabling Compression (Server-Side):
Compression is typically enabled on the web server. You don’t need to change your code files themselves. The server compresses the files before sending them to the browser.
Conclusion
Minification and compression are two essential techniques for optimizing your website’s performance. They’re relatively easy to implement, and the benefits in terms of reduced file sizes and faster loading times are substantial. By combining these techniques with other optimization strategies (like image optimization), you can create a significantly faster and more user-friendly website.
